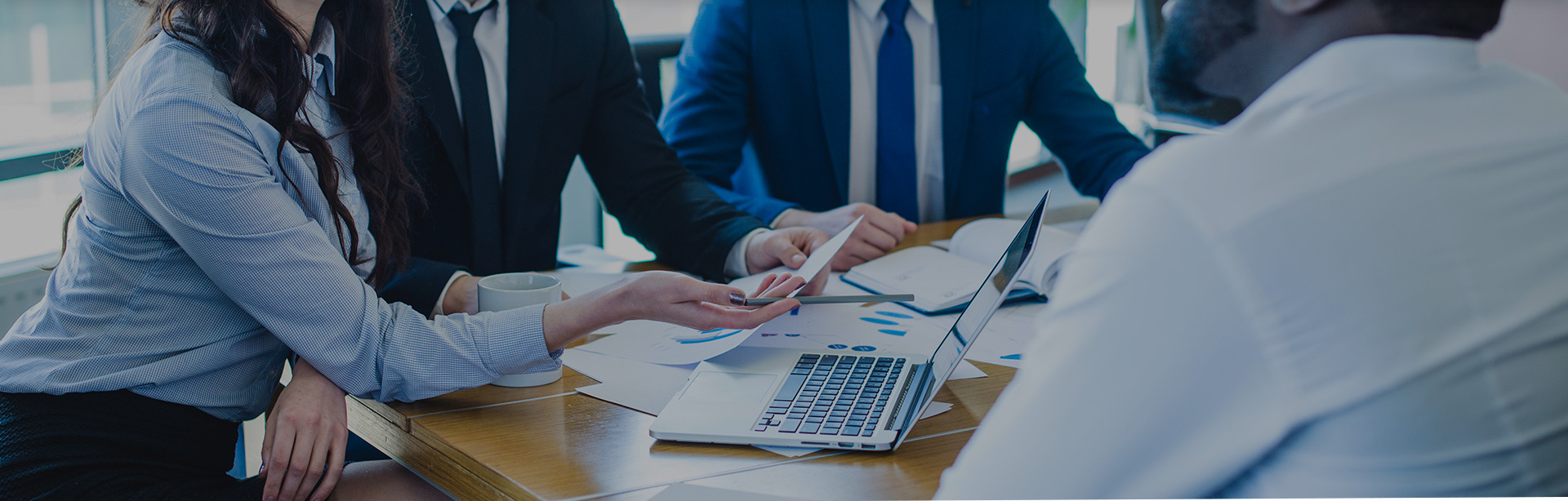
News and Events
•••Hot news
•••-
The key to ensure the long-term stable operation of the standard inverter DC arc welding machine
-
Welding Parameters Optimization and quality Control of Stainless Steel MIG Welding Wire
-
Advancements in Welding Electrode Technology and Their Impact on the Industry
-
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Welding Electrodes and Their Solutions
-
An In-depth Look into the Raw Materials and Manufacturing Processes of Carbon Steel MIG Welding Wires
Common Defects And Preventive Measures Of Aluminum Alloy Welding
Dec 19,2024
1. Welding pores
During welding, the bubbles in the molten pool fail to escape when solidifying, and the holes remain.
Causes:
1) There is oil stain on the surface of the base metal or welding wire material, the oxide film is not clean, or not welding in time after cleaning.
2) The purity of the shielding gas is not high enough, and the protection effect is poor.
3) The air supply system is not dry, or leaks air and water.
4) Improper selection of welding process parameters.
5) Poor gas protection during the welding process, and the welding speed is too fast.
Preventive measures:
1) Thoroughly clean the weld area and welding wire before welding.
2) Qualified shielding gas is used, and the purity should meet the specifications.
3) The air supply system is kept dry to prevent air and water leakage.
4) The selection of welding process parameters should be reasonable.
5) Pay attention to maintain the accurate position between the welding torch, the welding wire and the workpiece, and the welding torch should be perpendicular to the workpiece as much as possible; Try to use short arc welding, and the distance between the nozzle and the workpiece should be controlled at 10~15 mm; The welding torch should move in a straight line at a uniform speed, and the tungsten electrode should be aligned with the center of the weld, and the wire should be fed at a constant speed in reciprocating; There should be wind blocking facilities at the welding site, and there should be no wind flow, and the weldments should be properly preheated; Pay attention to the quality of arc striking and arc closing.
2. Not welded through, not fused
The phenomenon of incomplete penetration during welding is called incomplete penetration.
The part between the weld bead and the base metal or between the weld bead and the weld bead that is not completely melted and bonded during welding is called unfused.
Causes:
1) The welding current control is too small, the arc is too long, the welding speed is too fast, and the preheating temperature is low.
2) The weld gap is too small, the blunt edge is too large, and the groove angle is too small.
3) The oxide on the surface of the weldment and between the weldment layer is not clean.
4) The operation technology is not proficient, and the good time for wire feeding can not be grasped.
Preventive measures:
1) Select the correct welding current parameters. When the thick plate is welded, the workpiece is preheated at 80~120 °C before welding, so that the temperature of the workpiece meets the welding requirements.
2) Choose the appropriate weld joint clearance and groove angle.
3) Strengthen the cleaning of oxides on the surface of the weldment and between the welding layers.
4) Strengthen the welding operation technology, should correctly judge the melting situation of the groove or the surface of the welding layer, and adopt the method of fast welding and fast sending less welding wire by using high current (generally the welding part should be able to obtain a clean and bright molten pool of a certain size within 5 s after the arc ignition, and wire welding can be added at this time), and the careful welding can avoid the occurrence of unwelded penetration and non-fusion.
3. Undercut
After welding, the concave groove at the junction between the base metal and the edge of the weld is called the undercut.
Causes:
1) The welding process parameters are too large, the welding current is too large, the arc voltage is too high, and the heat input is too large.
2) The welding speed is too fast, and the welding wire leaves the molten pool before it has time to fill the arc pit, and undercut will occur.
3) The swing of the welding torch is uneven, the angle of the welding torch is too large when welding, and the swing is not in place, which will also cause undercut.
Preventive measures:
1) Adjust and reduce the welding current or arc voltage.
2) Appropriately increase the wire feeding speed or reduce the welding speed and residence time at the edge of the weld pool to make the weld bead filled.
3) Appropriately reduce the melt width, increase the penetration depth, and improve the depth-width ratio of the weld, which has an obvious effect on inhibiting undercut defects.
4) The welding operation should make the welding torch swing evenly.
4. Tungsten clipping
The non-metallic impurities that remain in the weld metal during welding are called slag inclusions. Tungsten clamping occurs when the tungsten electrode melts and falls into the molten pool due to excessive current or collision with the workpiece welding wire.
Causes:
1) The cleaning before welding is not thorough, and the melting end of the welding wire is seriously oxidized, resulting in slag inclusion.
2) Improper selection of tungsten end shape and welding parameters leads to burn of the end and produces tungsten inclusion.
3) The welding wire is in contact with the tungsten electrode and the oxidizing gas is misused.
Preventive measures:
1) Mechanical and chemical cleaning methods can be used to remove oxides and dirt from the groove and welding wire; With high-frequency pulse arc starting, the melting end of the wire is always in the protected area.
2) The welding current should match the shape of the tungsten terminal.
3) Improve the operation skills, avoid the contact between the welding wire and the tungsten electrode, and update the inert gas.
5. Burn through
Due to the high temperature of the molten pool and the untimely filament filling, the welded molten metal flows out of the groove and forms a perforation defect.
Causes:
1) The welding current is too large.
2) The welding speed is too slow.
3) The groove form and assembly clearance are unreasonable.
4) The technical level of welder operation is low.
Preventive measures:
1) Reduce the welding current appropriately.
2) Increase the welding speed appropriately.
3) The groove processing should conform to the specification, adjust the assembly clearance, increase the blunt edge, and reduce the root clearance.
4) Improve operating techniques.
6. Overburning and oxidation of the weld bead
Severe oxidation products occur on the inner and outer surfaces of the weld bead.
Causes:
1) The tungsten electrode is not concentric with the nozzle.
2) The gas protection effect is poor, the gas purity is low, and the flow rate is small.
3) The melt pool temperature is too high.
4) The tungsten pole extension is too long, and the arc length is too large.
Preventive measures:
1) Adjust the concentricity of the tungsten electrode and the nozzle.
2) Ensure the purity of the gas and increase the gas flow rate appropriately.
3) Increase the current appropriately, increase the welding speed, and fill the wire in time.
4) The tungsten electrode extension is appropriately shortened, and the arc length is reduced.
7. Cracks
Under the action of welding stress and other factors, the gap caused by the destruction of the metal atom binding force in the local area of the welded joint.
Causes:
1) The welding structure is unreasonable, the weld is excessively concentrated, and the welded joint is too restricted.
2) The size of the molten pool is too large, the temperature is too high, and the alloying elements are burned out.
3) The arc is closed too fast, the arc pit is not filled, and the welding wire is withdrawn too fast;
4) The welding material fusion ratio is not suitable. When the melting temperature of the welding wire is too high, it will cause liquefaction cracks in the heat-affected zone.
5) Improper selection of welding wire alloy composition; When the magnesium content in the weld is less than 3%, or the iron and silicon impurity content exceeds the specified level, the crack tends to increase.
6) The arc pit is not filled, and the arc pit cracks appear
Preventive measures:
1) The design of the welded structure should be reasonable, the weld layout can be relatively dispersed, the weld should avoid stress concentration as much as possible, and the welding sequence should be reasonably selected.
2) Adopt a relatively small welding current, or appropriately speed up the welding speed.
3) The arc closing operation technology should be correct, and the arc closing place can be added with a lead plate to avoid the arc closing too fast, and the current attenuation device can also be used to fill the arc pit.
4) Choose the welding material correctly. The composition of the selected wire should be matched to the base metal.
5) Add an arc striking plate or use a current attenuation device to fill the arc pit.
And what can we do for you?
Do you have questions about the cetecom advanced services, are you interested in a consultation or would you like to get a concrete offer? Just contact us directly. Our team of experts is looking forward to your message.

We offer a variety of top-quality welding consumables, welding accessories, welding machine for shipbuilding, aviation, nuclear power, pipeline, pressure vessel, steel structure, container, engineering machinery etc.
- Products Welding Consumables Welding Machine
- Solutions Welding Consumables Welding Machine
- quick links Cases News & Events Company
-
Contact
Email: info@tsuntec.com
Telephone:+86 150 6396 2790
whatsapp: 8615063962790
Address:No 2 South Hei Long Jiang Road, Shibei District, Qingdao, China