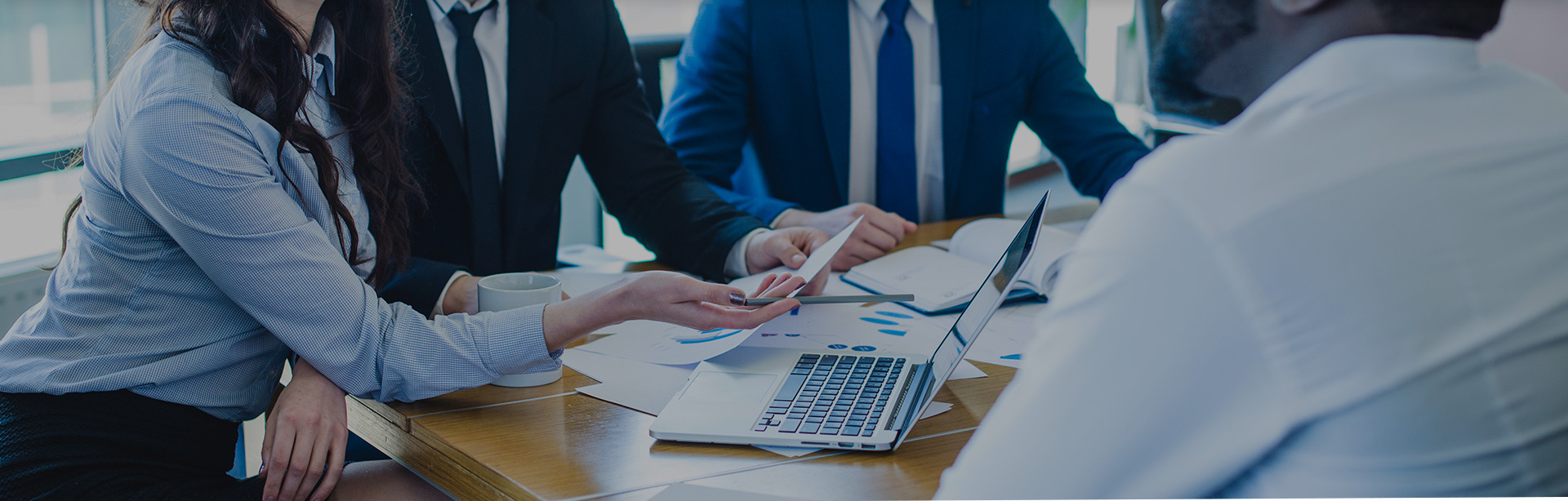
News and Events
•••Hot news
•••-
The key to ensure the long-term stable operation of the standard inverter DC arc welding machine
-
Welding Parameters Optimization and quality Control of Stainless Steel MIG Welding Wire
-
Advancements in Welding Electrode Technology and Their Impact on the Industry
-
Troubleshooting Common Issues with Welding Electrodes and Their Solutions
-
An In-depth Look into the Raw Materials and Manufacturing Processes of Carbon Steel MIG Welding Wires
Classification And Selection Of Welding Equipment And Welding Consumables
Jan 10,2025
1. Classification of welding equipment
(1) Electrode arc welding equipment
Electrode arc welding equipment mainly includes welding machine, welding power supply, welding tongs, welding cables and ground wire clamps.
(2) Tungsten inert gas shielded welding equipment
Manual tungsten inert gas shielded welding equipment is mainly composed of welding power supply, welding gun, gas supply system, water cooling system, welding cable and remote control.
1)According to the degree of automation of welding operations, tungsten inert gas shielded welding equipment can be divided into two categories: manual and automatic.
2) According to the type of welding current, it can be divided into DC, AC and pulse current tungsten inert gas shielded welding equipment.
3) CO₂ gas shielded welding equipment
CO₂ gas shielded welding equipment is mainly composed of welding power supply, welding gun, wire feeding mechanism, gas supply system and control system.
4) Submerged arc welding equipment
Submerged arc welding equipment can be divided into three categories: mechanized, automatic and fully automatic according to the degree of automation of the welding process.
Submerged arc welding machine consists of: welding trolley and head moving mechanism, wire feeder, welding wire correction and pressing mechanism, welding power, control system, etc.
5) Electroslag welding equipment
Electroslag welding equipment is mainly composed of welding power supply, machine head, electronic control system, and water-cooled forming (slide) block. Welding methods can be divided into: wire electroslag welding, plate electroslag welding, and fuse electroslag welding.
(6) Stud welding equipment
Stud welding equipment is divided into two categories: arc stud welding and capacitance energy storage discharge stud welding according to its power supply type and welding method. The arc stud welding machine is composed of a welding power supply, a controller, a welding gun, a ground pliers, a welding cable and other parts.
7) Welding robot
Welding robot is a collection of machinery, computers, sensors, artificial intelligence and other aspects of knowledge and technology in one of the modern, automated equipment.
The welding robot is mainly composed of two parts: the robot and the welding equipment. The robot consists of a robot body and a control cabinet (hardware and software). The welding equipment is composed of welding power supply (including its control system), wire feeder (arc welding), welding gun (pliers) and other parts. For intelligent robots, there are also sensing systems, such as laser or camera sensors and their control devices.
2. Application of popular welding equipment
1) Application of electrode arc welding machine
It has been widely used in various types of welded structure manufacturing industry. Such as in the construction of steel structure manufacturing and installation, shipbuilding, marine engineering structure manufacturing, oil and gas pipeline installation and construction, large liquefied gas storage tank construction, special equipment and chemical equipment
Manufacturing and other aspects still occupy an important position.
2) Application of tungsten inert gas shielded welding machine
Tungsten inert gas shielded welding machine is a high-quality arc welding equipment, which has been widely used in the production of various welded structures.
(1) There are many types of metal materials used. In addition to low melting point, volatile metal materials (such as lead, zinc, etc.), tungsten inert gas shielded welding machine can be used for welding.
(2) Applicable joint thickness range. The joint range used in conventional tungsten inert gas shielded welding is 0.5~4.0mm.
(3) Suitable for various welding positions. These include flat welding, flat fillet welding, horizontal welding, vertical welding, and vertical welding, as well as all-position welding of joints in horizontally fixed pipe fittings. Because air convection, passing wind, and breeze may destroy the protection of the gas on the welding area, auxiliary windproof facilities should be configured during field construction.
(4) It can be used for welding automation. On the basis of manual self-melting and manual wire filling, tungsten inert gas shielded welding equipment can be equipped with a variety of mechanized and automated welding equipment for mechanized, automated and fully automated welding, and can also be integrated with the welding robot system to achieve welding automation.
3) CO₂ gas shielded welder application
CO₂ gas shielded welding is a welding technology that is mainly promoted in China, which is mainly used for welding of low carbon steel and low alloy steel, and is also suitable for surfacing welding of vulnerable parts and repair welding of steel castings. Electrode arc welding and submerged arc welding have been gradually replaced in the production of many metal structures.
3. Welding Consumables
1) Classification and selection of welding rods
(1) Welding rod classification
① According to the composition of the electrode coating: titanium oxide type, titanium calcium type, iron oxide type, low hydrogen type, cellulose type, graphite type, ilmenite type, salt base type eight categories.
②Classification by use: structural steel electrodes, molybdenum and chromium-molybdenum heat-resistant steel electrodes, low-temperature steel electrodes, stainless steel electrodes, surfacing electrodes, cast iron electrodes, nickel and nickel alloy electrodes, copper and copper alloy electrodes, aluminum and aluminum alloy electrodes, and special purpose electrodes.
③ Classified according to the properties of slag: alkaline electrodes (also known as low-hydrogen electrodes) and acid electrodes.
④ Classified according to special properties: ultra-low hydrogen electrode, low dust and low toxicity electrode, vertical downward electrode, bottom electrode, iron powder high-efficiency electrode, moisture-resistant electrode, underwater electrode, gravity electrode, upward electrode, etc.
(2) Welding rod selection requirements
① The selection of welding rods should be selected according to the requirements of the design documents when the design is specified.
② When the design is not specified, it should meet the premise of structural safety and reliable use, in order to improve the working conditions and improve the technical and economic benefits as the principle, comprehensively consider the following factors: steel chemical composition and mechanical properties, weld metal properties, steel structure characteristics (plate thickness, joint form) and stress state, manufacturability, welding position and welding conditions (indoor, field, space size), welding workload (weld length, weld equivalent).
(3) The principle of electrode selection
① The principle of matching the mechanical properties and chemical composition of the weld metal. The regulations require that the strength of the weld metal and the base metal is equal, and the tensile strength of the deposited metal should be equal to or slightly higher than that of the base metal. For alloy steels, the weld metal alloy composition is required to be the same or close to the base metal. In the unfavorable situation that the rigidity of the welded structure is large, the joint stress is high, and the weld is prone to cracks, the welding rod with lower strength than the base metal should be considered. When the content of carbon, sulfur, phosphorus and other elements in the base metal is high, the weld
It is easy to produce cracks, so low-hydrogen electrodes with good crack resistance should be selected.
For example: when selecting welding materials for steel structure engineering, according to the design requirements, in addition to ensuring that the strength and plasticity of the welded joint are not lower than the lower limit value specified in the base metal standard, the impact toughness of the welded joint should also be guaranteed not to be lower than the lower limit of the impact toughness specified in the base metal standard.
② The principle of ensuring the performance and working conditions of welded components. For the weldments bearing dynamic load and impact load, in addition to meeting the strength requirements, the main thing should be to ensure that the weld metal has high plasticity and toughness, and low-hydrogen electrodes with high plastic and toughness indicators can be selected. For weldments in contact with corrosive medium, stainless steel electrodes or other corrosion-resistant electrodes should be selected according to the properties and corrosion characteristics of the medium. Weldments working under high temperature, low temperature, wear-resistant or other special conditions should be selected with corresponding heat-resistant steel, low-temperature steel, surfacing welding or other special-purpose welding rods.
③ Meet the characteristics of welded structure and the principle of stress conditions. For thick and large weldments with complex structure shape and large rigidity, in the welding process, the cooling speed is fast, the shrinkage stress is large, and the cracks are easy to occur, so the welding rod with good crack resistance, good toughness, high plasticity and low hydrogen cracking tendency should be selected.
For example: low-hydrogen electrodes, ultra-low-hydrogen electrodes and high-toughness electrodes.
④ It has the principle of operability of welding process. When the welding part of the weldment cannot be turned over, the welding rod suitable for all-position welding should be selected. For the weldments that are not stressed much and the welding parts are difficult to clean, acid electrodes that are not sensitive to rust, oxide scale and oil should be selected. When there is no DC welding machine, it is necessary to choose an electrode that can be used for both AC and DC. In the occasion of narrow or poor ventilation conditions, acid electrodes or low-dust electrodes should be selected under the condition of meeting the performance requirements.
⑤ The principle of improving productivity and reducing costs. When acid electrodes and alkaline electrodes can meet the requirements, acid electrodes should be selected as much as possible. For structures with a large amount of welding workload, high-efficiency electrodes should be selected as much as possible when conditions permit.
For example: iron powder electrode, gravity electrode, bottom electrode, vertical down electrode and high-efficiency stainless steel electrode, etc. This is not only conducive to the improvement of productivity, but also conducive to the stability and improvement of welding quality.
4. Characteristics and types of tungsten electrode materials
(1) Tungsten electrode material characteristics
The electrode material used for manual tungsten argon arc welding should have strong electron emission ability, can form a stable arc, has high temperature resistance, is not easy to evaporate and lose at high temperature of the arc, can withstand large welding current, has sufficient strength and wear resistance, etc.
(2) Types of tungsten electrodes
① Pure tungsten electrode. It is one of the earliest electrode materials used, with a tungsten electrode melting point of 3387 °C and a boiling point of 5900 °C. Due to the high voltage required for pure tungsten electrode emitting electrons, the welder is required to have a high no-load voltage. In addition, pure tungsten is easily burned, so it is gradually replaced by thorium tungsten electrode.
② Thorium tungsten electrode. Add 1%~2% thorium oxide to pure tungsten, which is thorium tungsten electrode. It has high thermal electron emission capacity and flux resistance, has the performance of easy arcing, low no-load voltage required, and the allowable current can be increased by 1/3 compared with the pure tungsten electrode of the same diameter, and is not easy to burn out, and has a long service life. However, the dust of thorium tungsten electrode has trace amounts of radioactivity, so labor protection measures must be strengthened when grinding the electrode.
③ Cerium tungsten electrode. Cerium oxide of less than 2% is added to pure tungsten, which is cerium tungsten electrode. It has more advantages than thorium tungsten electrode, easy arc initiation, stable arc, slender arc beam, heat concentration, maximum allowable current density can be increased by 5%~8%, small burning loss, long life. Since cerium tungsten electrode has almost no radioactive hazards, cerium tungsten electrode is currently the most widely used electrode material.
Commonly used tungsten electrodes (rods) have a variety of diameters such as 0.5mm, 1.6mm, 2.4mm, 3.2mm, 4.0mm and 5.0mm.
5. Welding wire classification and selection
Welding wire classification
(1) Classification according to cross-sectional structure: it can be divided into two categories: solid wire and flux cored wire.
(2) Classification according to the type (grade) of the welding wire: the gas shielded welding wire is divided by the model, and the submerged arc welding wire is divided by the grade.
The principle of welding wire selection
(1) The welding wire shall be selected according to the specified code.
(2) Solid welding wire is mainly used for tungsten gas shielded welding and MIG/MAG welding; The composition of the solid welding wire is mainly considered to be that the weld metal should be well matched with the mechanical or physical properties of the base metal, such as wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and the weld should be dense and defect-free.
(3) Flux-cored wire is used for MIG/MAG welding with CO₂ and Ar+CO₂ as shielding gases, the former is used for ordinary structures, and the latter is used for important structures.
(4) Self-shielding flux-cored wire is similar to welding rod, without additional gas shielded welding, wind resistance is better than gas shielded welding, usually can be welded under four-level wind, suitable for field or high-altitude work, has been widely used in foreign construction industry, and has also been applied in the welding of long-distance oil and gas pipelines in China. In the current standard of flux-cored wire in China, the type category of self-protection flux-cored wire occupies a large proportion.
6. Classification and application of welding gas
Welding gas classification
(1) Gas for gas welding and cutting: combustible gas (O₂); Combustible gas: acetylene, propane, petroleum gas, natural gas, etc.
(2) Welding shielding gases: carbon dioxide (CO₂), argon (Ar), helium (He), nitrogen (N), oxygen (O₂) and hydrogen (H₂).
Application of welding gas
(1) The choice of welding gas mainly depends on the welding and cutting method. In addition, it is also related to the properties of the welded metal, the quality requirements of the welded joint, the thickness of the weldment and the welding position and the process method.
(2) When nitrogen arc welding, N is used as the shielding gas, and copper and stainless steel can be welded. N is also commonly used for plasma arc cutting as an outer shielding gas.
(3) H₂ is used as a reducing gas, which is mixed with O₂ during welding and burned as a heat source for gas welding.
(4) The mixed gas is generally selected according to the welding method, the material to be welded and the influence of the mixing ratio on the welding process.
For example, when welding low-alloy high-strength steel, it is hoped that pure Ar will be used as the shielding gas to reduce oxide inclusions and oxygen content in the weld. Starting from the stabilization arc and weld shaping, it is hoped to add oxidizing gas to Ar.
7. Flux classification and application
(1) Classification of fluxes
① According to the different classification of production process: flux can be divided into melting flux, bonding flux and sintering flux.
② According to the classification of deoxidizer and alloying agent added to flux: flux can be divided into neutral flux, reactive flux and alloy flux.
The different types of fluxes can be identified by the respective grades and the manufacturer's product instructions.
(2) Submerged arc flux application
The flux used in submerged arc welding is an important welding material, and its welding process performance and chemical metallurgical properties are the main factors that determine the weld metal.
8. Re-inspection requirements for welding materials
(1) Re-inspection of welding materials of steel structures
The welding materials used in the first-class weld of the first-class and second-class welds of the building structure safety level of the first-class and second-class welds of the building structure of the first-class and second-class welds of the building structure of the building structure of the first-class and second-class welds, the first-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-class welds of the first-class and second-level welds of the first-class and second-level welds of the first-class and second-class welds of
(2) Re-inspection of welding materials for special equipment
Electrodes and flux-cored wires used for spherical tanks should be retested for diffused hydrogen according to the batch number. Welding rods, welding wires, and fluxes can only be used after passing the re-inspection after the expiration date.
And what can we do for you?
Do you have questions about the cetecom advanced services, are you interested in a consultation or would you like to get a concrete offer? Just contact us directly. Our team of experts is looking forward to your message.

We offer a variety of top-quality welding consumables, welding accessories, welding machine for shipbuilding, aviation, nuclear power, pipeline, pressure vessel, steel structure, container, engineering machinery etc.
- Products Welding Consumables Welding Machine
- Solutions Welding Consumables Welding Machine
- quick links Cases News & Events Company
-
Contact
Email: info@tsuntec.com
Telephone:+86 150 6396 2790
whatsapp: 8615063962790
Address:No 2 South Hei Long Jiang Road, Shibei District, Qingdao, China